Microarea Analysis
Microarea analysis using X-ray diffraction (XRD)
As electronic components continue to shrink in size, the regions targeted for X-ray diffraction (XRD) analysis are also becoming smaller. Consequently, there is a growing demand for microarea analysis using X-rays focused into a small, point-like beam. To meet this demand, two primary methods are commonly used to reduce the X-ray beam size.
1. Using slits or collimators
This method involves extracting only the central portion of a line-shaped beam using slits or collimators. By replacing these components with ones of different sizes, the beam size can be easily and flexibly adjusted to suit specific analytical requirements. However, this approach has a major drawback: since most of the beam is blocked, the resulting X-ray intensity is significantly reduced. Additionally, when using long collimators, care must be taken to avoid interference between the sample and the collimator, particularly at low 2θ angles.
2. Using X-ray focusing optics (CBO-f, CBO-μ)
In this method, as illustrated in Figure 1, a line-shaped parallel beam is focused into a point-shaped beam using specialized optics. Compared to the slit/collimator method, this approach results in less intensity loss, enabling faster microarea analysis. However, the focused beam size is fixed for each optical element. For example, the CBO-f, which uses a polycapillary lens, produces a beam with a diameter of approximately φ0.5 mm at the sample position. The CBO-μ, which uses a multilayer confocal mirror, achieves a beam diameter of about φ0.1 mm. These sizes are estimated based on the full width at half maximum (FWHM) of the direct beam intensity distribution.
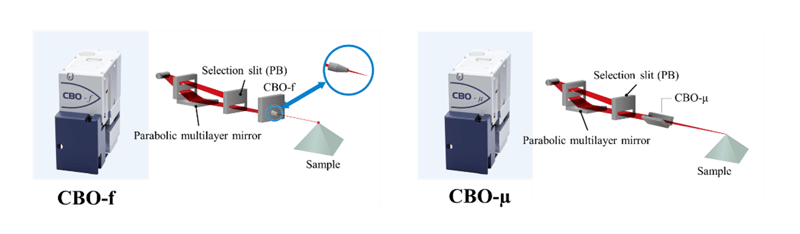
Figure 1: X-ray focusing optics in SmartLab: Left) CBO-f, Right) CBO-μ
When compared to beams of similar size formed using collimators, the CBO-f can deliver approximately 40 times higher intensity, while the CBO-μ provides about 10 times higher intensity. This significant increase in intensity greatly enhances the efficiency of micro-area analysis.
Further enhancing data intensity
By combining a microfocused incident X-ray beam with a two-dimensional detector, it is possible to integrate the diffraction intensity along the Debye ring. This technique enables the acquisition of even higher intensity data, further accelerating the microarea analysis process.
Rigaku recommends the following products

Contact Us
Whether you're interested in getting a quote, want a demo, need technical support, or simply have a question, we're here to help.
