Application Note B-XRD1071
Introduction
The Scherrer method is a typical method for evaluating the crystallite size of powder samples. The method assumes that the broadening of diffraction peaks due to crystal lattice strain can be ignored, and calculates the crystallite size based on the fact that the crystallite size in the direction perpendicular to the lattice plane of the diffraction peak is inversely proportional to the full width at half maximum of the peak. Cerium oxide (CeO₂) is a functional oxide nanoparticle used as a base material for exhaust gas cleaning catalysts and transparent electrolyte sheets. Since the performance of these materials depends on the particle size and crystallite size of the CeO₂ nanoparticles, evaluating their sizes is very important. In this example, we measured the X-ray diffraction pattern of CeO₂ nanoparticles and evaluated the crystallite size using the Scherrer method.
Measurement and results
Calculation of crystallite size by the X-ray diffraction method is performed by measuring a standard sample containing sufficiently large crystallites and applying Scherrer equation to the difference in peak widths between the standard and measured sample. Figure 1 shows the X-ray diffraction patterns of the measured sample CeO₂ nanoparticles (average particle size is 10 nm), and the standard sample of CeO₂ containing large crystallites. When the crystallite size was calculated from the integrated widths of peaks using the Scherrer equation, the crystallite size in the direction perpendicular to each (hkl) was calculated as 8.9 to 9.2 nm (Table 1). The obtained values were approximately equal to the average particle size, which indicates that the CeO₂ nanoparticles are single crystals with the particle size nearly identical to the crystallite size. 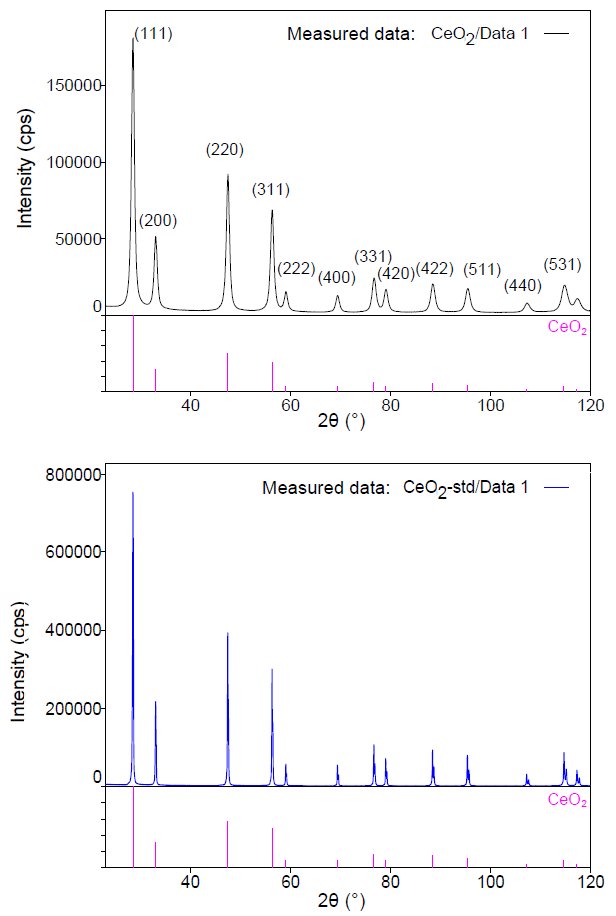 Figure 1: X-ray diffraction patterns of the measured sample (top) and standard sample (bottom)
Figure 1: X-ray diffraction patterns of the measured sample (top) and standard sample (bottom)
Table 1: Crystallite size of CeO₂ nanoparticles
| (h k l) | Crystallite size (mm) |
| CeO₂ (1 1 1) | 9.08(4) |
| CeO₂ (2 0 0) | 8.79(8) |
| CeO₂ (2 2 0) | 9.16(5) |
| CeO₂ (3 1 1) | 9.18(7) |
| CeO₂ (2 2 2) | 9.1(2) |
| CeO₂ (4 0 0) | 9.10(18) |
| CeO₂ (3 3 1) | 8.88(14) |
| CeO₂ (4 2 0) | 9.2(2) |
| CeO₂ (4 2 2) | 8.98(14) |
| CeO₂ (5 1 1) | 8.95(16) |
| CeO₂ (4 4 0) | 9.1(3) |
| CeO₂ (5 3 1) | 9.13(17) |

