Application Note POLYMER001
Introduction
The performance of resins and films varies greatly depending on their internal crystal structure and degree of crystallinity. However, these structural differences cannot be ascertained by appearance or general physical property measurements. X-ray diffractometer (XRD) is a technique that can visualize and quantify the internal crystal structure of a sample without destroying it, enabling “visualization” of crystallinity in the field of material development and product verification.
Crystal phase analysis
| Analysis: | Raw and intermediate materials |
| Analyzed materials: | Polypropylene |
| Use: | Material development |
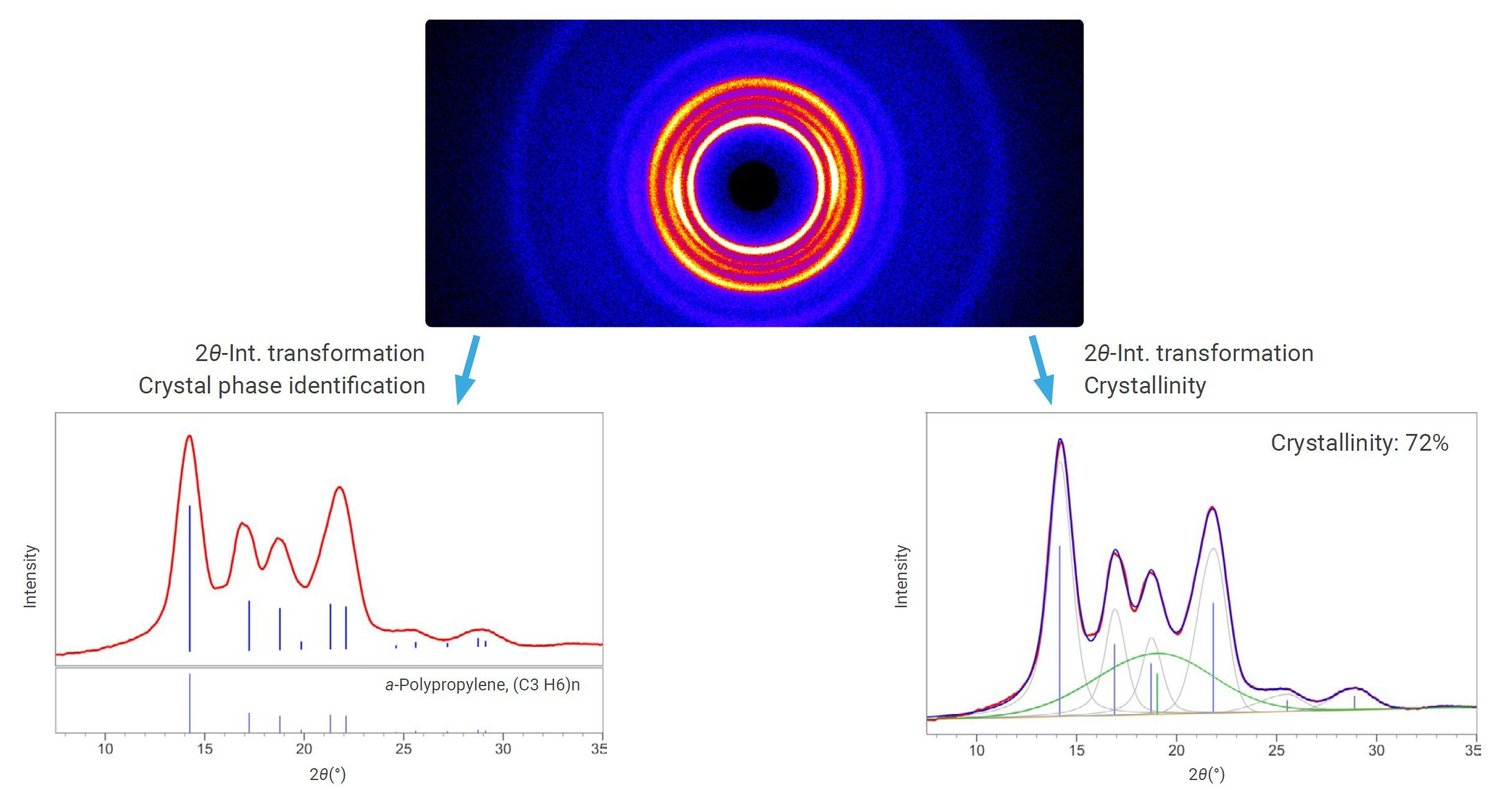
Figure 1: (Top) 2D measurement of polypropylene; (Lower left) 1D profile and crystalline phase identification of polypropylene; (Lower right) Crystallinity calculation of polypropylene
Conclusion
Transmission 2D XRD measurements were performed on polypropylene and the obtained data were used as the primary XRD data. By converting to the original profile, the crystalline phase was identified and the degree of crystallinity was calculated (Figure 1). In this measurement, the characteristic diffraction peak of polypropylene was clearly observed, and the degree of crystallinity was quantified to be approximately 72% from the diffraction peak fitting process. Thus, this method is advantageous in that it allows nondestructive and rapid quantitative evaluation of structure

