What is Vapor Phase Decomposition (VPD)?
Vapor Phase Decomposition (VPD) is a sample pretreatment technique used to analyze trace elements present on the surface of semiconductor substrates such as silicon wafers. This method is commonly employed as a pretreatment step for analytical instruments such as ICP-MS (Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry) and TXRF (Total Reflection X-ray Fluorescence).
TXRF is a non-destructive, high-sensitivity analytical method that involves irradiating mirror-like surfaces—such as silicon wafers—with X-rays at extremely low incident angles, allowing for the detection of trace surface elements. However, depending on the specific processes used in semiconductor manufacturing, even higher sensitivity may be required. In such cases, pretreatment using VPD can enhance the detection sensitivity of TXRF by up to a factor of 100.
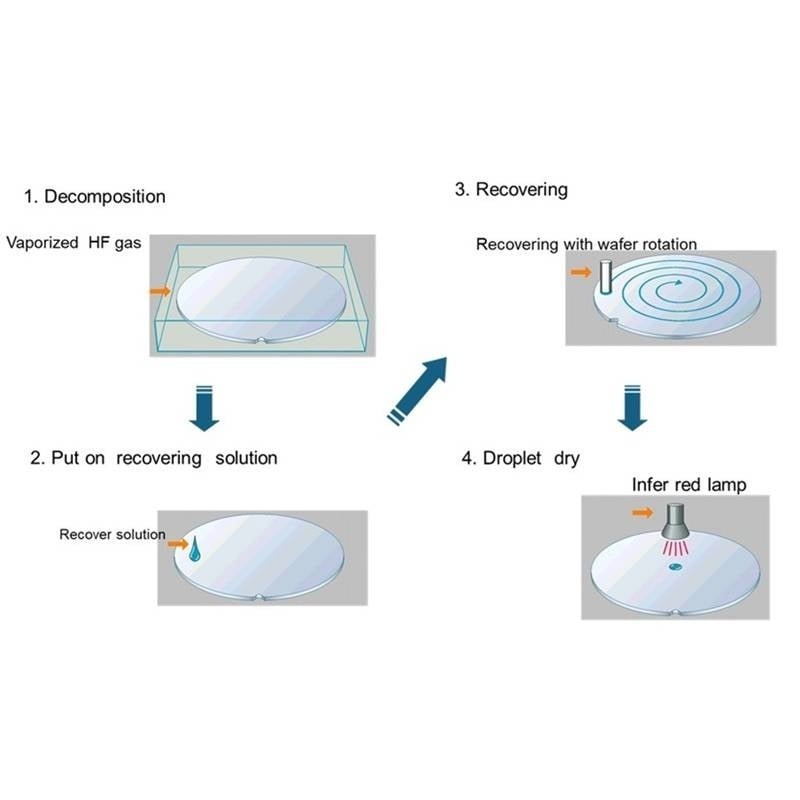
In the VPD process, hydrofluoric acid (HF) vapor is first used to decompose the surface oxide layer of the substrate. Then, a recovering liquid is applied to recover metallic and other contaminant elements from the decomposed oxide. After drying the collected residue, TXRF measurements are performed. Since the contaminants are concentrated during the collection and drying steps, the resulting fluorescence X-ray intensity increases, thereby improving analytical sensitivity.
Rigaku recommends the following products

Contact Us
Whether you are interested in getting a quote, want a demo, need technical support, or simply have a question, we're here to help.
