Application Note B-XRI1032
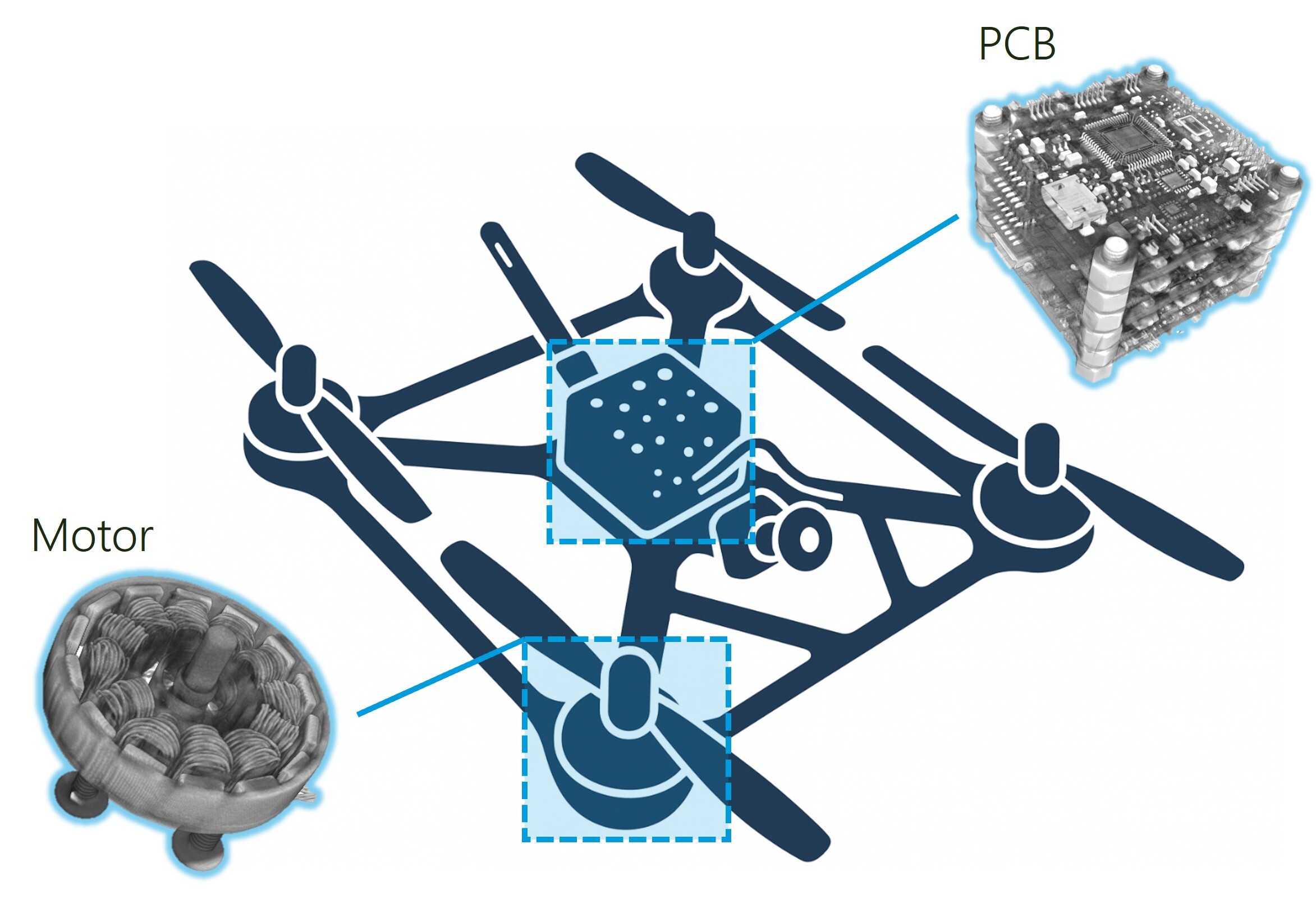
About the sample: VTOL drone
Drones of various sizes and functions have been increasingly utilized in a wide spectrum of applications, ranging from remote site monitoring to excavation scouting, unmanned delivery, professional video shooting and recreational uses. With emerging market demanding drones with a wide range of shapes, sizes, and different functions, a reliable way to obtain the drone’s comprehensive 3D structure information is crucial for design improvement and timely problem solving to support an agile manufacturing process.
X-ray CT (X-ray computed tomography) is a non-destructive 3D characterization tool that captures internal structural details from large assembled parts to small electrode connections. In this application note, a commercial VTOL drone was scanned to reveal the condition of different assembly parts as well as the circuit in the central control unit.

Analysis procedure
- In this example, a VTOL drone was scanned using a CT scanner, CT Lab HV.
- CT images were used to look at the full assembly to inspect areas of interest.
- Enhanced high-resolution CT scans for central PCB boards were rendered for closer investigation, with the propeller motor coils segmented for thickness analysis.
1. CT scan
The VTOL drone was scanned with CT Lab HV using 225 kV and 1.0 mm Tin filter. A large field of view (FOV) scan with voxel resolution of 125.43 µm was performed first to examine structure information on the entire VTOL drone. Zoomed in scans focusing on the center PCB assembly and propeller motor were then performed to provide higher resolution images for further detailed structure inspection of key components. Full scan of the drone is intentionally omitted in this application note for proprietary reasons.
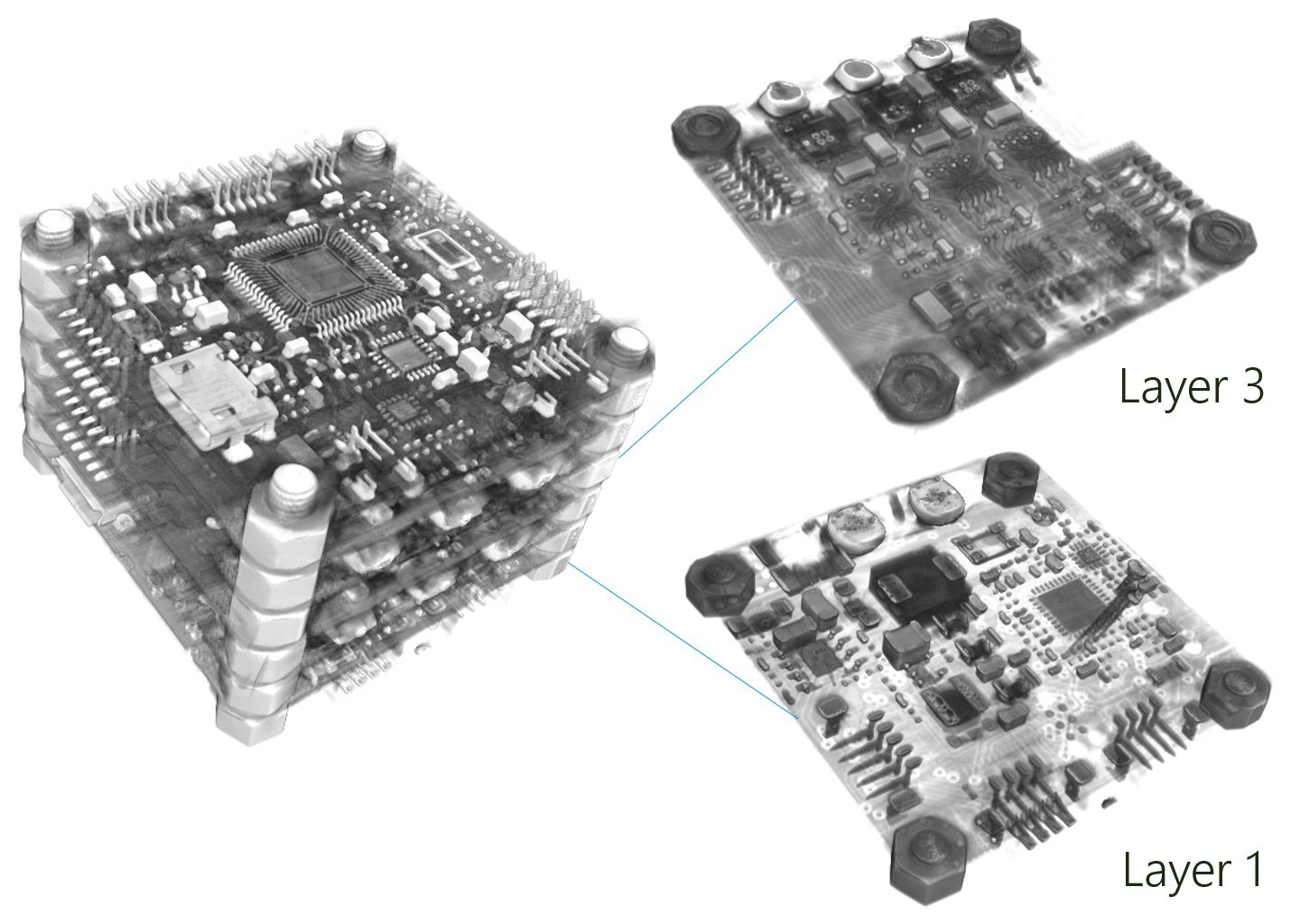
2. PCB inspection
A zoomed-in scan focusing on the central PCB assembly was performed with a voxel resolution of 63.28 µm. With 3D volumetric data, it is possible to virtually disassemble individual PCB layers for targeted analysis.
2D cross-section views of selected angles are shown with corresponding color, providing comprehensive information on the assembly build quality.
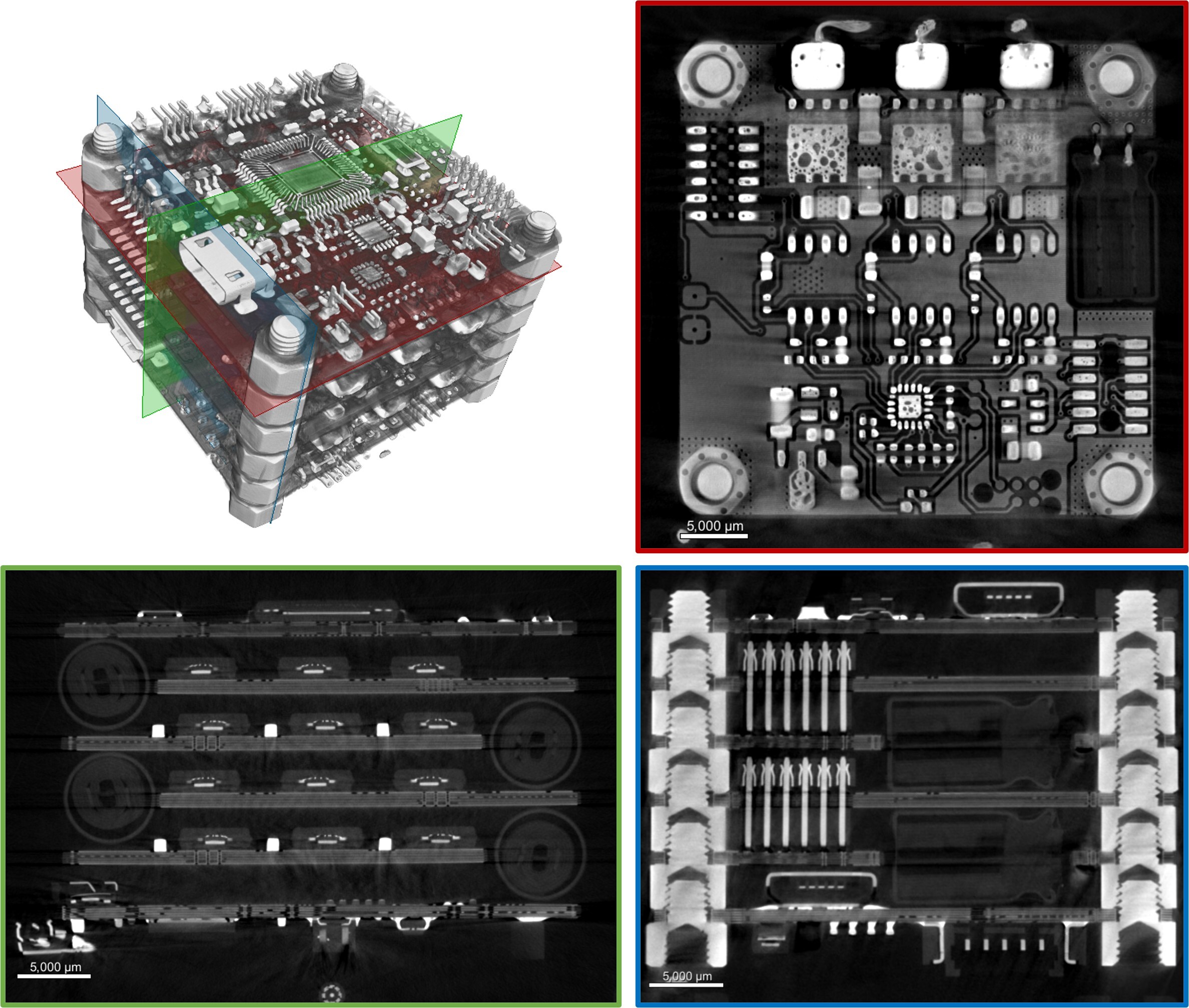
3D render video demonstrates the zoomed-in detail scan on the central PCB assembly.
3. Motor assessment
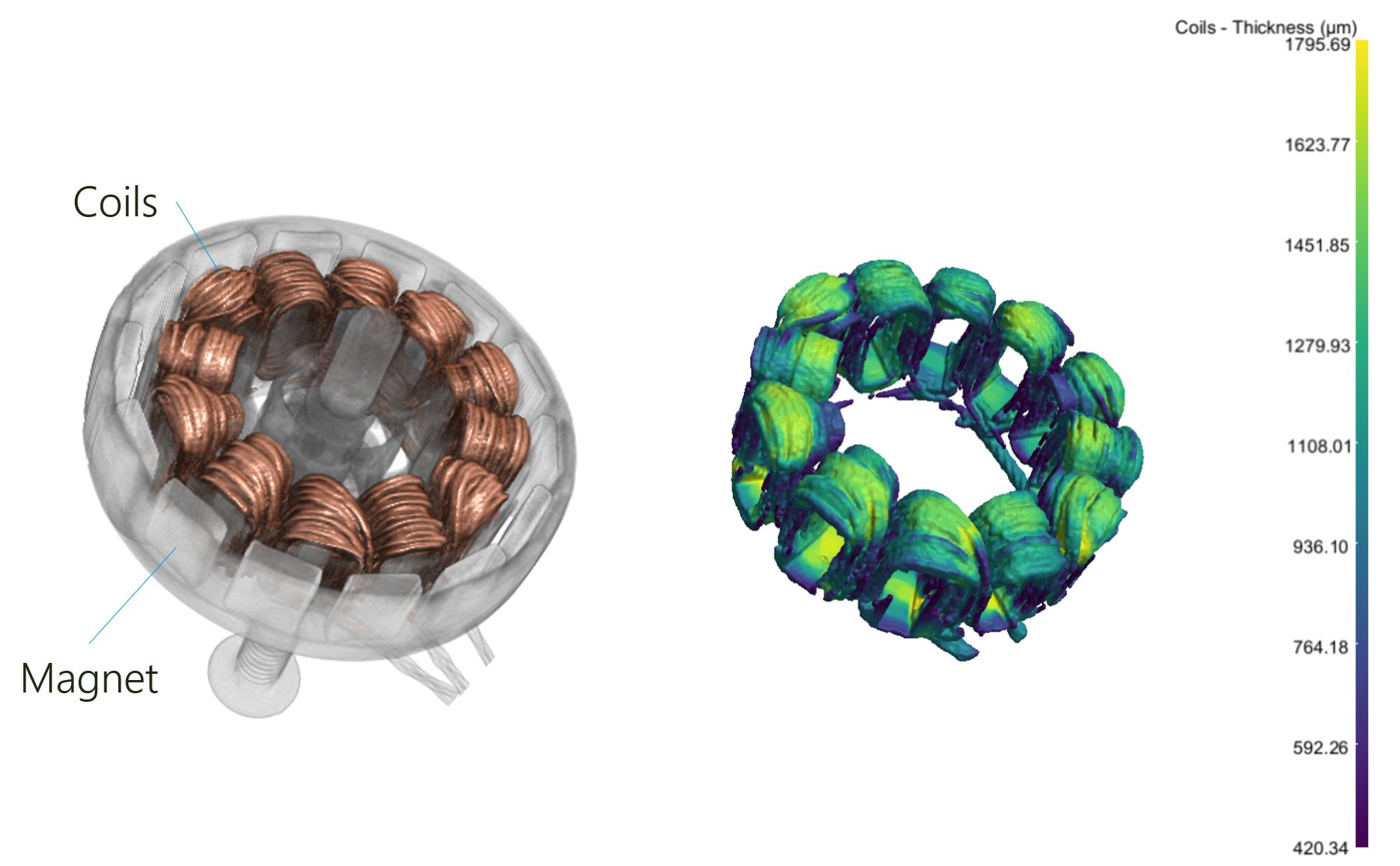
A high-resolution scan with voxel size of 74.29 µm was performed focusing on the propeller motor. A 3D rendering as well as 2D cross-section views are shown below. Individual wires of the motor coils are clearly visible for inspection of any distribution faults that may cause a propeller rotation issue.
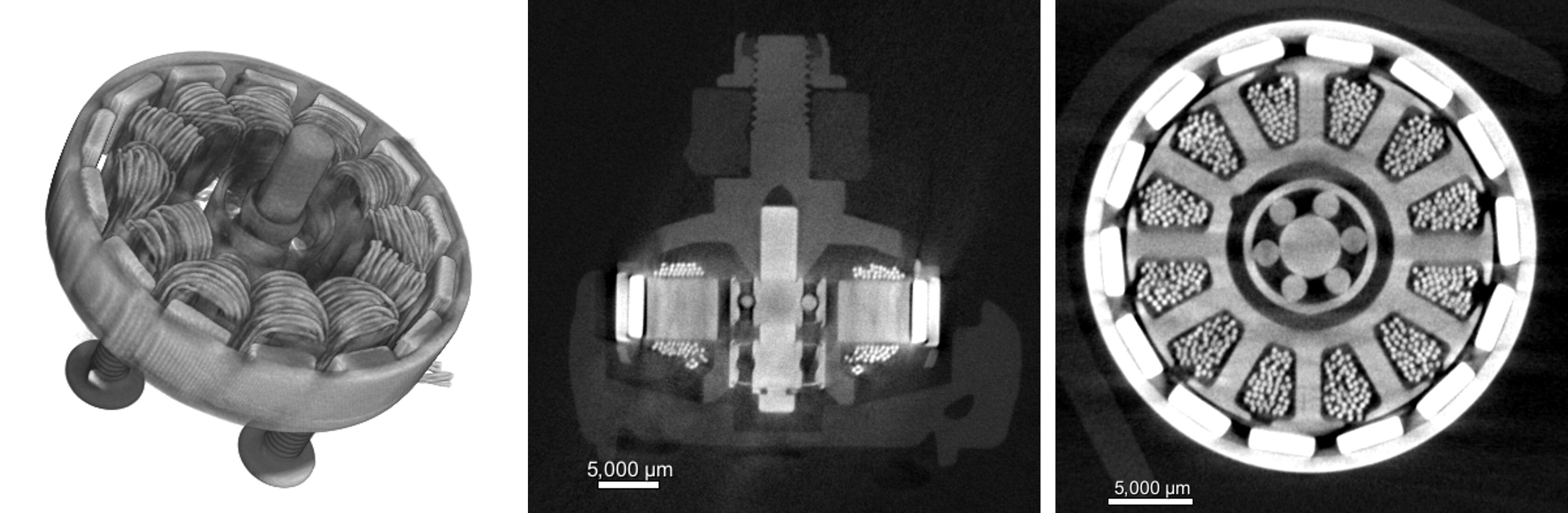
Segmentation of the motor coil was conducted using Dragonfly 3D World to enable quantitative assessment. A volume thickness analysis was calculated for the coil to highlight any anomaly, such as a loose bundle or broken segments.
Conclusions
This application note demonstrates how X-ray CT imaging can be used for inspecting VTOL drone samples. The entire VTOL drone structure was examined non-destructively using the CT Lab HV, providing critical insights into manufacturing quality. Focused, high-resolution scans enable detailed local examinations without requiring any additional sample alteration. Analysis, such as volume thickness, reveals internal part condition and potential faulty components. The scan results demonstrate how CT provides the benefits of advanced 3D imaging to allow product evaluation and design optimization for complex components in advanced manufacturing industries.

