Application Note POLYMER009
Introduction
The crystallinity of polymers is closely related to material properties such as stiffness, heat resistance, and processability, so it is essential to have an accurate understanding of the crystallinity of polymers. However, in the field, there are many cases where the crystallinity is judged based on empirical rules or catalog values, and there is a risk that the basis for product design and material selection becomes ambiguous. The DSC evaluation of the melting energy enables the quantification of the degree of crystallinity, which leads to improved design accuracy and prevention of problems.
Thermal analysis
| Analysis: | Raw materials and parts products |
| Use: | Process control, failure analysis, quality assurance |
| Analyzed materials: | High density polyethylene (HDPE) |
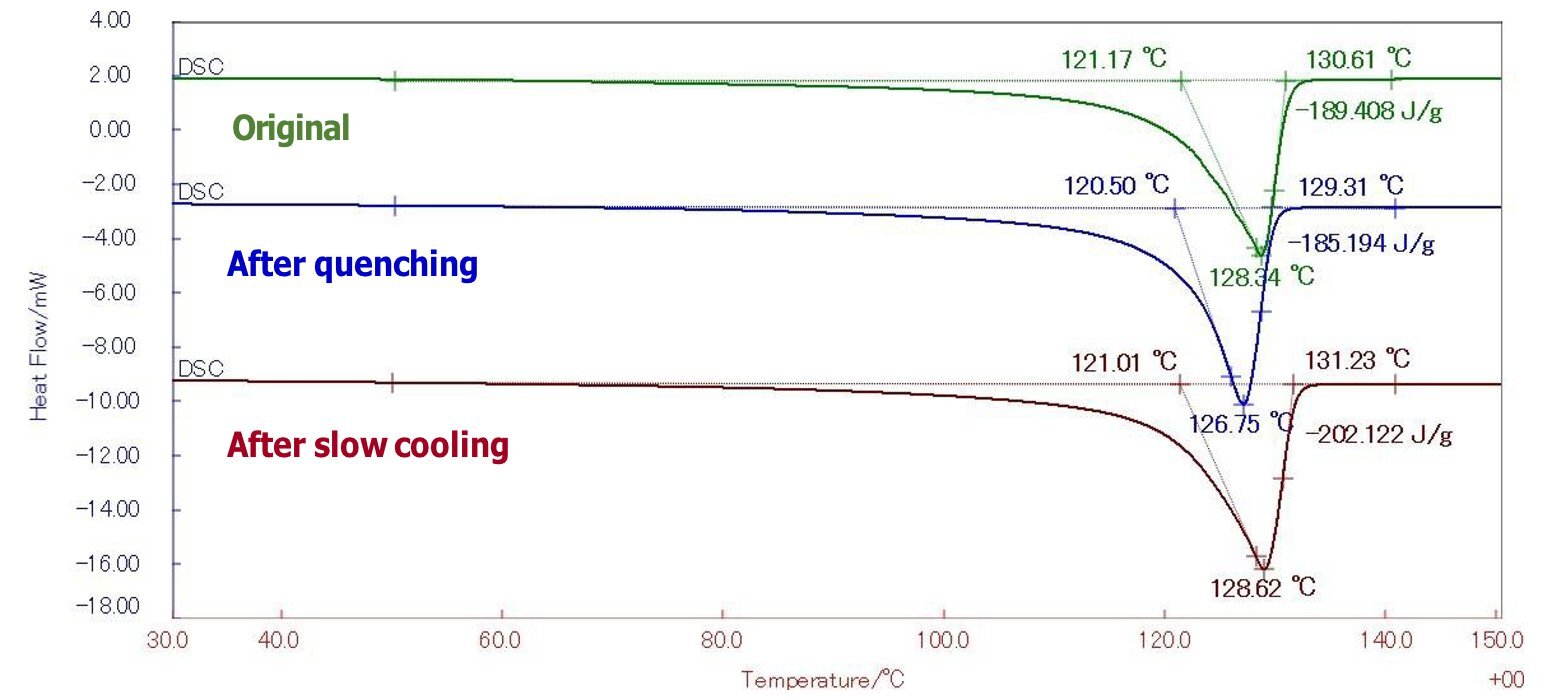
Figure 1: DSC results of HDPE
Table 1: Melting energy and crystallinity of HDPE
| Sample | Energy J/g | Crystallinity %HDPE | |
| HDPE | Original | 189.4 | 65.31 |
| After quenching | 185.2 | 63.86 | |
| After slow cooling | 202.1 | 69.69 | |
Conclusion
In HDPE, endothermic peaks due to melting appeared between 90 and 130°C. The melting energy of a perfectly crystalline HDPE is 290 J/g. Based on this, the degree of crystallinity can be determined from the energy of the endothermic peak due to the melting of each sample. By supporting the previously ambiguous judgment of crystallinity with numerical values, it is possible to provide a solid basis for material selection and review of design conditions.

