Sulfur in Bunker Fuel

Scope
The analysis of sulfur in bunker fuel and diesel per ASTM D4294 is demonstrated.
Background
Sulfur content is regulated in many petroleum fuels oils, and plays an important role in fuel quality and control of polluting emissions. In the 1970s, the International Maritime Organization (IMO) formed its ship pollution rules at the International Convention on the Prevention of Pollution from Ships, known as MARPOL 73/78.
Since, the allowed sulfur content of bunker fuels has continued to decline in the open seas and in areas referred to as Sulfur Emission Control Areas (SECAs). SECAs are defined protected areas in which only low sulfur bunker fuels and marine diesels can be used. Therefore, it is critical to monitor the sulfur content to ensure regulatory compliance and to improve air quality, affecting those utilizing as well as producing and supplying bunker fuels. To meet the needs of the industry, Rigaku offers NEX QC, a simple and versatile benchtop EDXRF analyzer for the analysis of sulfur and other elements in a wide variety of petroleum fuels, including bunker fuel and diesel. NEX QC is an important tool to meet the requirements for monitoring sulfur at these various levels, with the ability to measure sulfur over a broad range of concentrations and into the future as sulfur levels become even lower.
_picture_2020.06.25.jpg?width=800&height=610&name=800x610%20NEX%20QC%2B%20(S%20in%20Crude%20screen)_picture_2020.06.25.jpg) Model: NEX QC
Model: NEX QC
Sulfur in bunker fuel — Low range 0.10 – 1.00% S
Calibration
An empirical calibration was built using a set of commercially available certified bunker oil standards, which is similar to crude or residual oil. A summary of the calibration for 0.10 – 1.00% S is shown here.
| Element: S Units: % |
||
| Sample I.D. | Standard value | Calculated value |
| STD 1 | 0.10 | 0.098 |
| STD 2 | 0.30 | 0.304 |
| STD 3 | 0.50 | 0.499 |
| STD 4 | 0.70 | 0.698 |
| STD 5 | 1.00 | 1.001 |
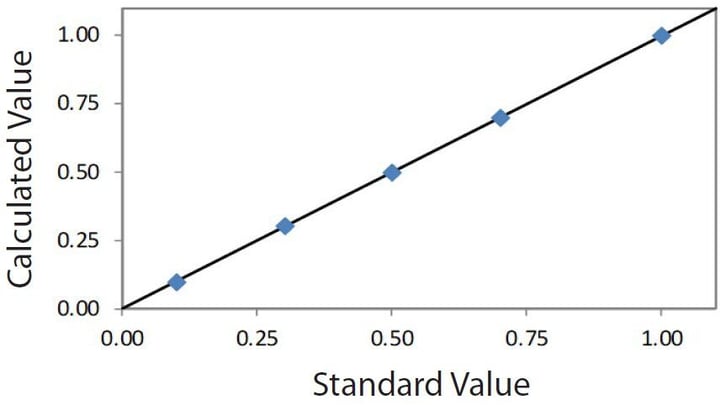 Correlation plot S
Correlation plot S
Repeatability
To demonstrate repeatability (precision), the select samples were chosen from the set of calibration standards. Each sample was measured in static position with typical results shown below.
| Element: S Units: % |
||||
| Sample I.D. | Standard value | Average value | Std. dev | % Relative |
| STD 1 | 0.10 | 0.0994 | 0.001 | 1.0 |
| STD 3 | 0.50 | 0.5035 | 0.003 | 0.6 |
Sulfur in bunker fuel — High range 0.50 – 5.00% S
Calibration
An empirical calibration was built using a set of commercially available certified bunker oil standards, which is similar to crude or residual oil. A summary of the calibration for 0.50 – 5.00% S is shown here.
| Element: S Units: % |
||
| Sample I.D. | Standard value | Calculated value |
| STD 6 | 0.50 | 0.505 |
| STD 7 | 1.00 | 0.994 |
| STD 8 | 2.50 | 2.488 |
| STD 9 | 3.00 | 3.011 |
| STD 10 | 4.00 | 4.015 |
| STD 11 | 5.00 | 4.988 |
.jpg?width=728&height=437&name=EDXRF1230%20Correlation%20plot%20S%20(high).jpg) Correlation plot S
Correlation plot S
Repeatability
To demonstrate repeatability (precision), the select samples were chosen from the set of calibration standards. Each sample was measured in static position with typical results shown below.
| Element: S Units: % |
||||
| Sample I.D. | Standard value | Average value | Std. dev | % Relative |
| STD 7 | 1.00 | 0.993 | 0.004 | 0.4 |
| STD 11 | 5.00 | 5.006 | 0.015 | 0.3 |
Sulfur in diesel — 0.10 – 1.50% S
Calibration
An empirical calibration was built using a set of commercially available #2 diesel fuel standards. A summary of the typical high range calibration is shown here.
| Element: S Units: % |
||
| Sample I.D. | Standard value | Calculated value |
| STD 1 | 0.10 | 0.099 |
| STD 2 | 0.30 | 0.295 |
| STD 3 | 0.50 | 0.498 |
| STD 4 | 0.70 | 0.708 |
| STD 5 | 1.00 | 0.996 |
| STD 6 | 1.50 | 1.500 |
.jpg?width=711&height=435&name=EDXRF1230%20Correlation%20plot%20S%20(diesel).jpg) Correlation plot S
Correlation plot S
Repeatability
To demonstrate repeatability (precision), the select samples were chosen from the set of calibration standards. Each sample was measured in static position with typical results shown below.
| Element: S Units: % |
||||
| Sample I.D. | Standard value | Average value | Std. dev | % Relative |
| STD 1 | 0.10 | 0.103 | 0.001 | 1.0 |
| STD 3 | 0.50 | 0.496 | 0.002 | 0.4 |
| STD 5 | 1.00 | 1.008 | 0.003 | 0.3 |
International standard test methods
The Rigaku NEX QC complies with the following international standards test methods for measuring sulfur in crude, bunker fuel, diesel, and other petroleum oils. Note that by weight 1 ppm = 1 mg/kg.
| ASTM D4294 | ISO 20847 | ISO 8754 | IP 496 | IP336 | JIS K 2541-4 |
| 16 ppm – 5% | 30 – 500 mg/kg | 100 mg/kg – 5% | 100 mg/kg – 5% | 100 mg/kg – 5% | 0.01 – 5% |
Conclusion
The performance shown here demonstrates the ability of the NEX QC to yield excellent results for the measurement of sulfur in bunker fuel and diesel in air, without the need for helium purge. The simple, modern touchscreen interface allows for reliable and efficient measurement protocols, and performance meets the major international norms shown on the left.

Contact Us
Whether you're interested in getting a quote, want a demo, need technical support, or simply have a question, we're here to help.
