A Study of the Stereochemistry of Sucrose and a Phenidate Derivative using the Copper Microfocus Source of the XtaLAB Synergy-i
Introduction to the benefits of Cu radiation
Cu Kα radiation is a useful source of radiation for general purpose X-ray diffraction experiments. Due to the approximate λ³ relationship with diffracted intensity, Cu Kα typically provides the strongest signal at the detector and thus enables faster experiments or easier study of small, weakly diffracting samples such as metal organic frameworks (MOFs). Due to the stronger anomalous signal obtained from Cu Kα radiation vs. other common wavelengths, it is possible to confirm the chirality for lighter atom structures—such as purely organic materials—with greater accuracy. Additionally, the longer wavelength of Cu Kα radiation can improve peak separation and consequently data quality for cases where reflection overlap is a concern; e.g., twinned crystals or long unit cell axes.
The XtaLAB Synergy-i (Figure 1) is a cutting-edge diffractometer equipped with the latest detector technology (HyPix Bantam), optimized for its small pixel size and sensitivity, and can be configured with up to two bright microfocus sealed tube X-ray sources. Herein, two datasets are presented and their results discussed. Both datasets were collected with the PhotonJet-i Cu source.
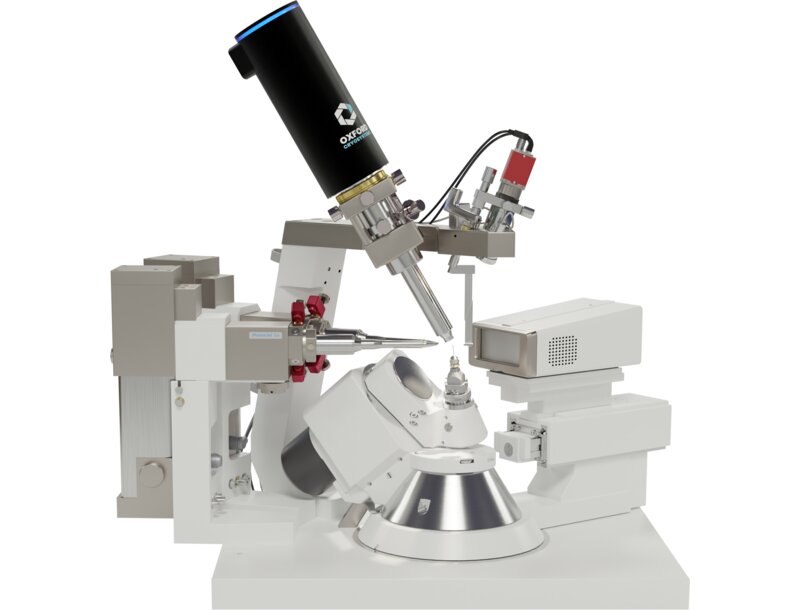

Figure 1: The XtaLAB Synergy-i.
Stereochemistry of sucrose
A sucrose crystal (0.10 x 0.16 x 0.31 mm) was mounted on a nylon loop and a 5-fold redundant dataset was planned at 100 K to obtain the best possible results for this chiral molecule. The high and low angle diffraction images can be seen in Figure 2 and further details about the data collection are shown in Table 1.
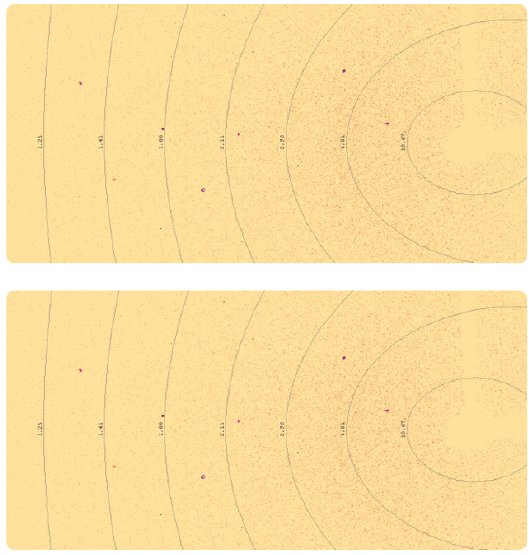
Figure 2: The low (top) and high (bottom) angle diffraction images from the sucrose data collection.
Table 1: Data collection details and data statistics.
| Experiment parameters | |
| Crystal-to-detector distance | 40 mm |
| Exposure time | 0.2 seconds |
| Total collection time | 51 minutes |
| Scan width / No. of frames | 0.5° / 9470 |
| Completeness | 99.9% (0.83 Å) |
| Average I/σ(I) | 82.17 |
| Redundancy [unmerged] | 5.0 |
Discussion
For this 1-hour data collection a redundancy of 5 was chosen to ensure a well-determined Flack parameter was achieved. For chiral molecules, like sucrose, the Flack parameter indicates if the model has been assigned the correct chirality. The Flack parameter here was 0.02(5), indicating with high certainty that the structure has the correct handedness.
Table 2: Data collection details and data statistics.
| Sucrose (C₁₂H₂₂O₁₁) | Monoclinic, P2₁ |
| Rint [unmerged data] | 2.40% |
| R₁ [unmerged data] | 1.98% |
| Flack parameter | 0.02 (5) |
Figure 3: Sucrose molecule.
A theo-methylphenidate salt derivative crystal
A very thin, plate-like crystal of a theo-methylphenidate salt derivative (Figure 4) was investigated using Cu Kα radiation on the XtaLAB Synergy-i diffractometer at 100 K. The sample was weakly diffracting and required longer exposure times at high angles. Data collection details can be seen in Table 3.
Table 3: Data collection details and data statistics.
| Detailed parameters | |
| Crystal-to-detector distance | 40 mm |
| Exposure time min/max | 0.3 and 2 seconds |
| Total collection time | 1 h 3 min |
| Scan width / No. of frames | 0.5° / 2466 |
| Completeness | 99.9% (0.83 Å) |
| Average I/σ(I) | 28.28 |
| Redundancy | 2.6 |

Figure 4: Single crystal of a theo-methylphenidate salt derivative. Sample size: 0.06 x 0.19 x 0.23 mm.
Table 4: Crystal data and refinement statistics.
| Crystal system, space group | Monoclinic, C2/c |
| Empirical formula | C₁₅H₂₂ClNO₂ |
| Rint | 2.19% |
| R₁ | 3.27% |
| Largest residual peak/hole (eÅ⁻³) | 0.211 / -0.249 |
Discussion
The excellent final refinement results obtained from this sample (Table 4), illustrates the high flux and good data quality that can be obtained from the Cu microfocus PhotonJet-i source of the XtaLAB Synergy-i.
Conclusion
The XtaLAB Synergy-i equipped with the Cu microfocus PhotonJet-i source is capable of collecting data on chiral compounds and weakly diffracting crystal samples. The high sensitivity and small pixel size of the HyPix Bantam detector ensures the reflections are being measured with greater accuracy, which thus produces better overall data quality.

Contact Us
Whether you're interested in getting a quote, want a demo, need technical support, or simply have a question, we're here to help.
