Manganese in Gasoline by ASTM D5059 Part D
Scope
The analysis of manganese (Mn) in MoGas (motor gasoline) and AvGas (aviation gasoline) is demonstrated as per ASTM D5059 Part D XRF using Cartesian Geometry EDXRF.
Background
Methylcyclopentadienyl manganese tricarbonyl (called MMT or MCMT) is an anti- knock agent added to MoGas and AvGas to boost octane rating, replacing tetraethyl lead (TEL) in many regions of the world. In motor gasoline, the Mn content is typically between 50 - 500 mg/kg and can be as high as 3000 mg/kg (approximately 3 g/L) in AvGas. Reliably characterizing the Mn content of gasoline ensures optimum engine performance based on the engine’s compression ratio and other geometrical and mechanical operating conditions. To meet the needs of the industry, Rigaku offers simple and versatile benchtop EDXRF analyzers for the analysis of manganese in gasoline. For optimum results in the ultra-low range, NEX CG II achieves exceptional detection limits using Cartesian Geometry EDXRF.
Sample preparation
Ensure each sample is homogeneous and stable. Shake the sample gently and allow any bubbles to settle. Fill a 32 mm XRF sample cup with 4 g of sample to ensure consistent sample depth. Etnom® film (3 µm) is used, which does not degrade quickly with gasoline or oxygenated gasoline. The sample cup lid must be vented with a small hole to ensure vapor pressure does not build. Due to the high evaporation rate of gasoline, it is recommended to make the measurement immediately after filling the cup. (Note: Use of internal standard is not required.)
| Model | NEX CG II |
| X-ray tube | 50 W Pd anode |
| Excitation | Indirect with polarization monochromatic EDXRF |
| Detector | Large-area SDD |
| Analysis time | 300 sec * |
| Environment | Helium purge |
| Film | Etnom® 3 µm |
* Shorter measurement times can be used if the precision and ultralow detection limits demonstrated are not required.
Calibration
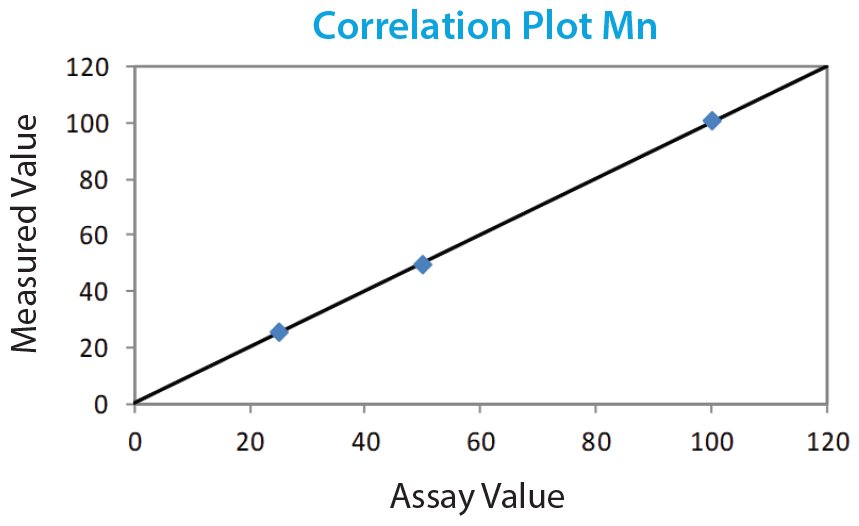
Empirical calibration is made using commercially available certified gasoline calibration standards containing the Mn additive. A calibration is shown here as a demonstration of the optimal performance using Cartesian Geometry for the low range 25 - 100 mg/kg Mn. The range can be extended up or down by adding appropriate standards to the calibration to cover desired Mn concentration range. Measurement time can be reduced if ultra-low precision and detection limits are not required.
| Units: mg/kg |
RMS Dev: 0.75 |
|
| Standard I.D. | Assay Value | Measured Value |
| 1 | 25 | 25.1 |
| 2 | 50 | 49.1 |
| 3 | 100 | 100 |
Precision
Instrument repeatability (precision) is determined by ten repeat analyses of each sample in static position using a 300 sec analysis time per measurement.
| Element: Mn | Units: mg/kg | |||
| Sample | Assay Value | Average Measured Value | Std. Dev | % Relative Deviation |
| 1 | 25 | 25.2 | 0.1 | 0.4% |
| 3 | 100 | 101 | 0.4 | 0.4% |
Detection limit
The lower limit of detection (LLD) is defined as three times the standard deviation of ten repeat analyses of a blank gasoline sample containing no Mn. The following typical LLDs are reported here using 100 and 300 sec measurement times.
| Element | LLD @ 100 sec | LLD @ 300 sec |
| Mn | 0.10 mg/kg | 0.06 mg/kg |
Conclusion
The results shown here indicate the Rigaku NEX CG II Cartesian Geometry EDXRF analyzer can be used to reliably measure Mn in MoGas (motor gasoline) and AvGas (aviation gasoline) at low and ultra-low levels as per ASTM D5059 Part D. Higher levels of Mn can easily be measured by extending the calibration and using shorter measurement time.


